September 3, 2020
Remove, Retire and Reserve with Finance4U

Kai Bi
Managing Director, Center of Excellence & Product Development
Public utilities provide essential and critical services to consumers, businesses, and societies. These services require advanced technologies and intensive investments. To ensure the high quality of services, public utilities are encouraged to continuously invest in utility assets; and within the investment, a large portion is to retire or replace aging assets.
Under the public utility accounting principle, removal and retirement are counted as capital investment, with special handling of accounting bookkeeping as compared to general accounting principles. According to FERC (Federal Energy Regulatory Commission), the costs incurred due to removal and retirement must be included in a reserve account, also known as the Accumulated Provision for Depreciation account, or simply called FERC 108. Reserve is further included into the rate base, through which the investments to removal and retirement can bring “return” to utilities. In the meantime, utility companies conduct depreciation studies in order to design asset depreciation rates that ensure not only the original construction costs, but also the removal and retirement costs can be “recovered.” As you can see, recording asset removal and retirement transactions and reporting them under the provision of reserve are critical for utility companies.
On the other hand, mass assets represent the majority of utility assets for electric transmission and distribution, gas, and water companies. It’s not easy to track information across EAM (Enterprise Asset Management), GIS (Geographic Information System) and Fixed Asset Accounting systems to determine the quantity, unit price, vintage and location of the portion of mass assets to retire. Even more challenging is to manage addition and retirement data over the years, with proper categorization of vintage, cost of removal, retirement and gross salvage to effectively support depreciation studies; or to support utilities’ need to continuously adjust their assets’ remaining life and depreciation rates in between depreciation studies to recover the gap between the actual reserve and estimated reserve.
SAP Fixed Asset (FI-AA) has been widely used in many industries as the fixed asset solution on the  SAP platform, offering solid, reliable and flexible functions to manage asset accounting. However, designed as a cross-industry module, FI-AA lacks support for utility-specific requirements. The handling of removal, retirement and reserve for mass assets is one of the critical issues.
SAP platform, offering solid, reliable and flexible functions to manage asset accounting. However, designed as a cross-industry module, FI-AA lacks support for utility-specific requirements. The handling of removal, retirement and reserve for mass assets is one of the critical issues.
Utegration Finance4U Extended Asset Accounting (formerly called Property and Lease Accounting) is an add-on directly in SAP S/4HANA that complements and enhances SAP Fixed Asset to address these requirements.
Finance4U’s Mass Asset Order function orchestrates the cost collection of removal work to the RWIP (Remove Work In Progress) asset. Upon retirement, it automatically generates retirement postings compliant to the public utility accounting standard, with cost of removal, retirement of both original cost and depreciation accrual, and gross salvage into the reserve account. Removal quantity is captured together with the dollar information. In case the vintage and unit price cannot be determined by EAM, Finance4U distributes the retirement vintage along the IOWA Curve, and deflates the retired unit price according to the Handy-Whitman Index.
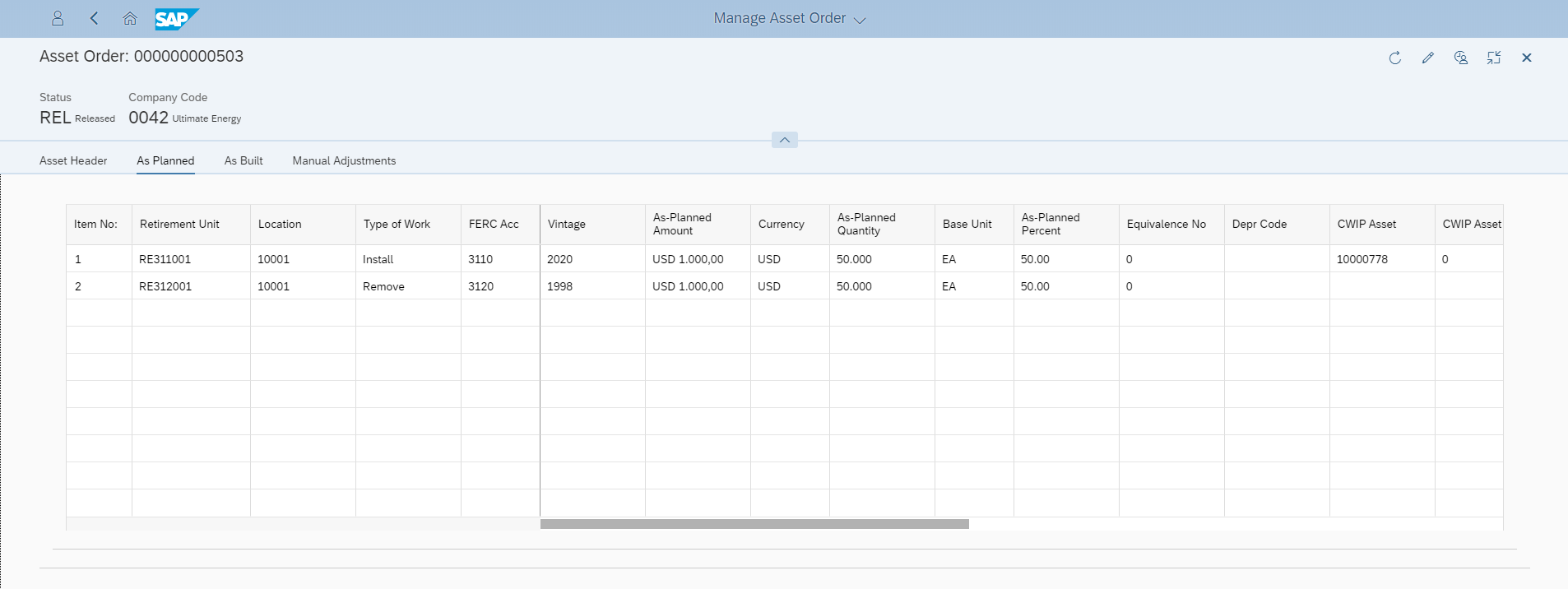
To address the unique challenges of mass assets, Finance4U utilizes the Continuing Property Records (CPR) function to categorize mass assets by vintage, asset location and by plant accounts or asset groups. Integrated with Finance4U, Mass Asset Order and CPR can list all the work history—including install or remove work orders, and manual adjustments. The balance of CPR is presented directly with FERC Account 101 (Plant In Service, PIS), 106 (Construction Completed Not Classified, CCNC), 107 (Construction Work In Progress, CWIP), and 108 (Reserve), demonstrating the complete lifecycle of the utility assets.
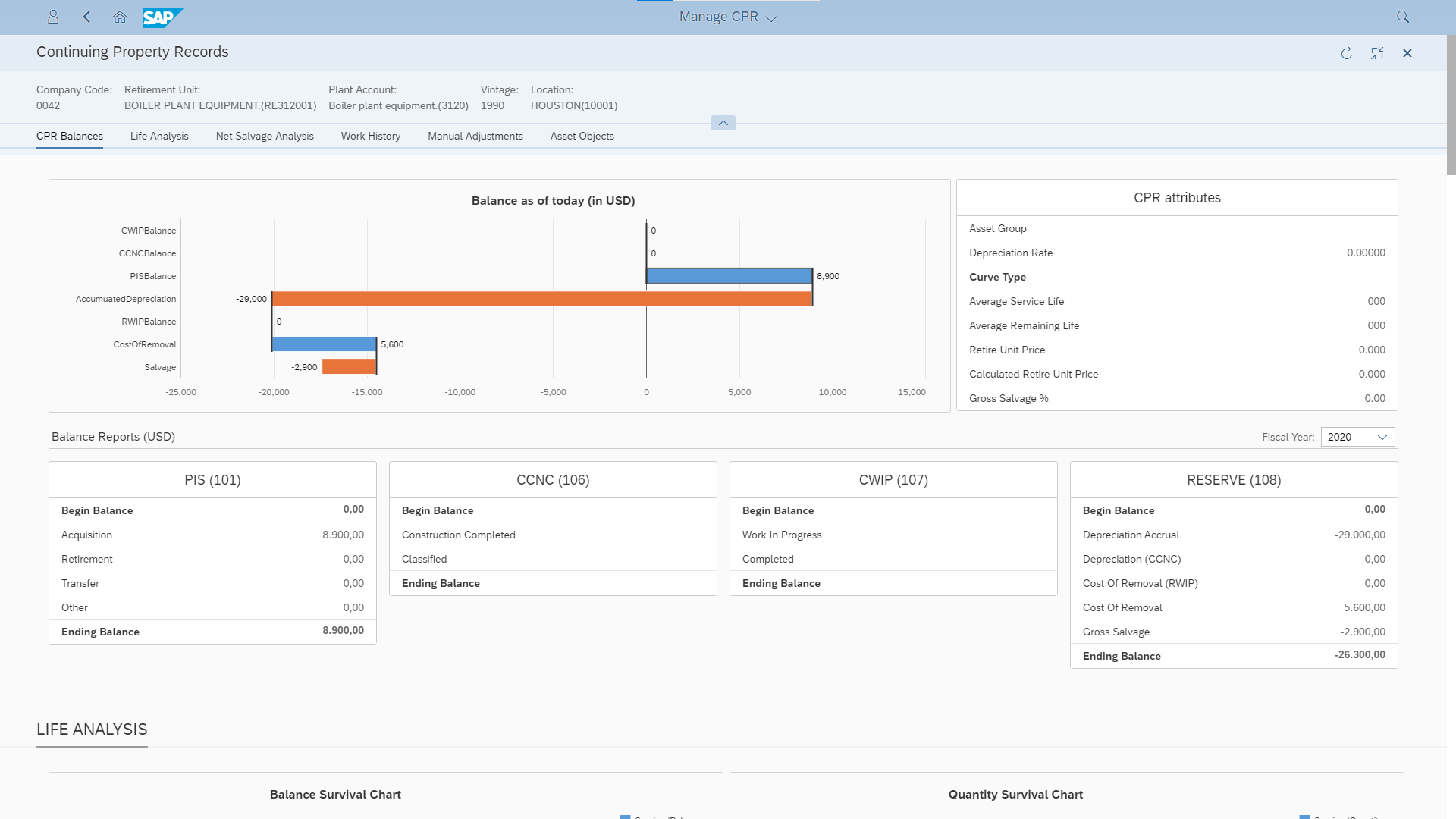
Being able to store and track the historical addition and retirement details by both fiscal year and vintage year, Finance4U provides thorough analytical capabilities on life analysis and net salvage analysis, which directly supports utilities’ depreciation study.
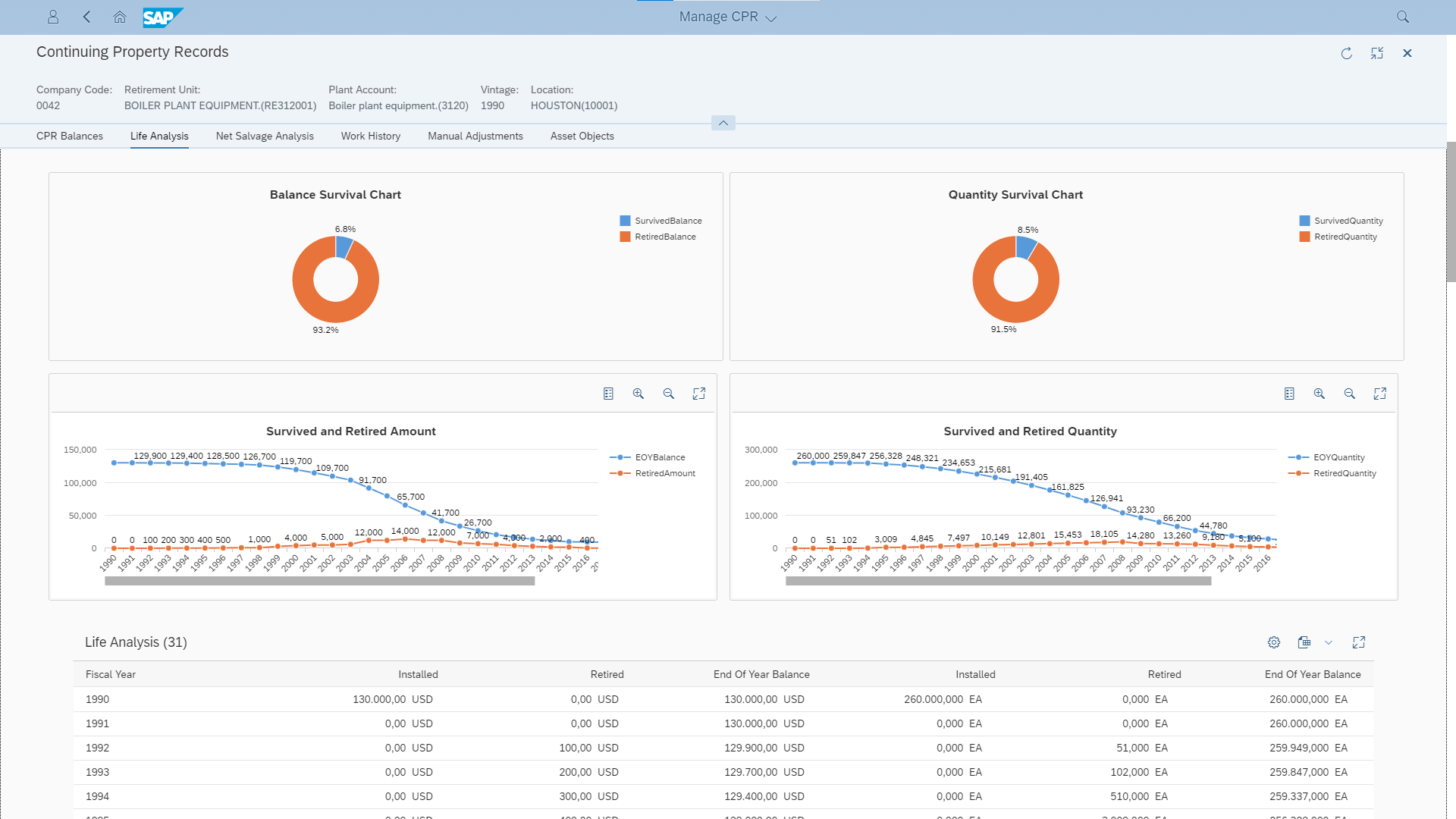
With this solid data foundation, even more advanced features are planned to be released by end of 2020. These include capabilities to automatically calculate mass asset average service life, remaining life and theoretic depreciation reserve.
Utegration Finance4U Extended Asset Accounting is an SAP-certified product working natively in SAP S/4HANA, enabling utility companies to address the core process of property accounting in a cost-effective way. It reduces data replication among systems, increases transparency and control and enables utilities to be compliant to the public utility accounting principle and new accounting standard, e.g. ASC 842 lease accounting standard. Perhaps best of all, the capitalization, retirement and month-end closing processes are automated, so that property accounting managers can focus more on analysis and decision making.
The product is available today in the SAP Store.
Hear NRG Share Their Experience
As part of their move to SAP S/4HANA, NRG optimized operations and financial accounting and reduced their total cost of ownership by using Utegration Finance4U Extended Asset Accounting. David Callen, Chief Accounting Officer of NRG, shares the story on this on-demand webinar.
Click here to view.
Learn More
Read the Finance4U Extended Asset Accounting solution overview or watch the video.
